How to operate a drone is a question increasingly asked as these versatile machines become more accessible. This guide delves into the intricacies of drone operation, from understanding regulations and safety protocols to mastering advanced flight techniques and capturing stunning aerial photography. We’ll cover everything you need to know, whether you’re a complete beginner or looking to refine your skills.
From pre-flight checks and battery charging to navigating complex maneuvers and troubleshooting common issues, this guide provides a structured approach to learning. We’ll explore the various components of a drone, explaining their functions and how they contribute to safe and efficient flight. We’ll also address the legal and ethical responsibilities involved in operating a drone, ensuring you fly responsibly and within the law.
Drone Regulations and Safety
Operating a drone responsibly requires understanding and adhering to both safety procedures and relevant regulations. These vary significantly depending on your location and the intended use of the drone, whether recreational or commercial. Failure to comply can lead to penalties, accidents, and damage to property.
Drone Licensing and Certification Requirements
Drone licensing and certification requirements differ widely across countries. In the United States, for recreational use, registration with the FAA is typically required for drones weighing over 0.55 pounds (250 grams). Commercial drone operation necessitates a Remote Pilot Certificate (Part 107). The European Union has its own drone regulations, categorized by drone weight and operational parameters, with various certifications needed for commercial use.
Countries like Canada and Australia also have their own specific licensing and registration frameworks. Always check the aviation authority in your specific country for the most up-to-date information.
Drone Safety Procedures
Safe drone operation involves a series of pre-flight, in-flight, and post-flight checks and procedures. Prior to each flight, it is crucial to thoroughly inspect the drone for any damage, ensuring the battery is adequately charged and the propellers are securely attached. During flight, maintain visual line of sight with the drone, avoiding obstacles and populated areas. After the flight, safely land the drone, power it down, and store it appropriately.
Preflight Inspection Checklist
A comprehensive pre-flight checklist should be followed for every flight, regardless of drone model. This checklist should include verifying battery charge, inspecting propellers for damage, checking the GPS signal strength, ensuring the remote controller is properly connected, and confirming that all sensors are functioning correctly. Specific checklists might vary depending on the drone model’s complexity and features.
International Drone Regulations Comparison
The following table compares regulations for commercial and recreational drone use in three different countries. Note that these are simplified examples and specific regulations are subject to change.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics, such as takeoff and landing procedures, is crucial before progressing to more advanced maneuvers. For a comprehensive guide on all aspects of safe and effective drone operation, check out this helpful resource on how to operate a drone and master the skills needed for responsible flying.
Remember, consistent practice and a thorough understanding of the regulations are key to becoming a proficient drone pilot.
| Country | Recreational Use | Commercial Use | Weight Restrictions |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | Registration required for drones over 0.55 lbs | Part 107 Remote Pilot Certificate required | Varies depending on airspace and operation |
| European Union | Categorized by drone weight and operational parameters | Specific certifications required depending on the category | Categorized (A1, A2, A3, etc.) with associated restrictions |
| Canada | Registration required for drones over 250 grams | Specific permits and certifications may be required | Varies based on operational category and location |
Parts of a Drone and Their Functions
Understanding the individual components of a drone is essential for both operation and maintenance. A typical quadcopter drone consists of several key parts working in coordination to achieve flight.
Key Components of a Quadcopter Drone
A standard quadcopter drone typically includes a flight controller, electronic speed controllers (ESCs), motors, a battery, propellers, a frame, and a camera (or other payload). The flight controller acts as the drone’s brain, processing data from various sensors and controlling the motors to maintain stability and execute flight commands. The ESCs regulate the power delivered to the motors, while the motors themselves generate the thrust needed for flight.
The battery provides the power source for the entire system. The frame protects the internal components, and the camera captures images or videos.
Component Functions, How to operate a drone
The flight controller receives data from the sensors (such as gyroscopes, accelerometers, and barometers), and uses this data to adjust the speed of each motor individually, ensuring stable flight and responsiveness to pilot commands. The ESCs regulate the power sent to the motors, allowing for precise control of speed and direction. The motors spin the propellers, generating the lift and thrust necessary for flight.
The battery provides the power for all the components.
Brushless vs. Brushed Motors
Brushless motors are generally preferred for drones due to their higher efficiency, longer lifespan, and greater power-to-weight ratio. Brushed motors are simpler and cheaper but less efficient, have a shorter lifespan, and generate more heat. Brushless motors require less maintenance, whereas brushed motors may require more frequent cleaning and replacement of brushes.
Internal Drone Component Diagram
Imagine a diagram showing a top-down view of a drone’s internal components. The flight controller is centrally located, surrounded by the four ESCs, each connected to a motor. The battery is typically positioned near the center of gravity. Wires connect all components, and the camera is mounted on a gimbal (in many models) for stabilized footage.
Preparing the Drone for Flight
Proper preparation is crucial for a safe and successful drone flight. This involves charging the battery correctly, calibrating the drone’s sensors, and establishing a connection with the remote controller and mobile application.
Drone Battery Charging
Always use the manufacturer-recommended charger for your drone’s battery. Never overcharge the battery, and avoid leaving it plugged in after it’s fully charged. Proper charging techniques help extend the battery’s lifespan and prevent potential safety hazards.
Compass and Sensor Calibration
Calibrating the drone’s compass and other sensors ensures accurate flight performance. The process typically involves following the instructions provided by the drone’s manufacturer, which often involves rotating the drone in a specific pattern to allow the sensors to accurately align themselves.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires a solid grasp of regulations and safe operating procedures. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, including practical tips and safety considerations, please refer to this excellent resource on how to operate a drone. Ultimately, responsible drone piloting ensures both safety and enjoyable flight experiences.
Connecting to Remote Controller and Mobile App
Connecting the drone to the remote controller usually involves powering on both devices and pairing them using the appropriate instructions. Connecting to a mobile app often involves downloading the app, creating an account, and connecting to the drone via Wi-Fi or Bluetooth. Ensure that the firmware of both the drone and the controller is updated to the latest version.
Essential Drone Accessories
Essential accessories for safe and effective drone operation include extra batteries, spare propellers, a carrying case, a screen protector for the remote controller, and possibly a carrying strap for the controller. Depending on the drone’s capabilities and intended use, additional accessories such as ND filters for the camera or a landing pad might be beneficial.
Basic Flight Controls and Maneuvers: How To Operate A Drone
Mastering basic flight controls is fundamental to safe and proficient drone operation. This section covers the techniques for takeoff, landing, hovering, and controlling altitude, direction, and speed.
Takeoff, Landing, and Hovering
Takeoff involves gently increasing the throttle until the drone lifts off the ground. Landing is the reverse process, gradually decreasing the throttle until the drone gently touches down. Hovering requires maintaining a constant throttle to keep the drone at a fixed altitude and position. Smooth and controlled movements are key to safe operation.
Altitude, Direction, and Speed Control
Most drone controllers have dedicated controls for altitude, direction, and speed. Altitude is typically controlled by a throttle stick, while direction is controlled by a joystick or directional pad. Speed is often adjustable through settings on the remote or mobile app.
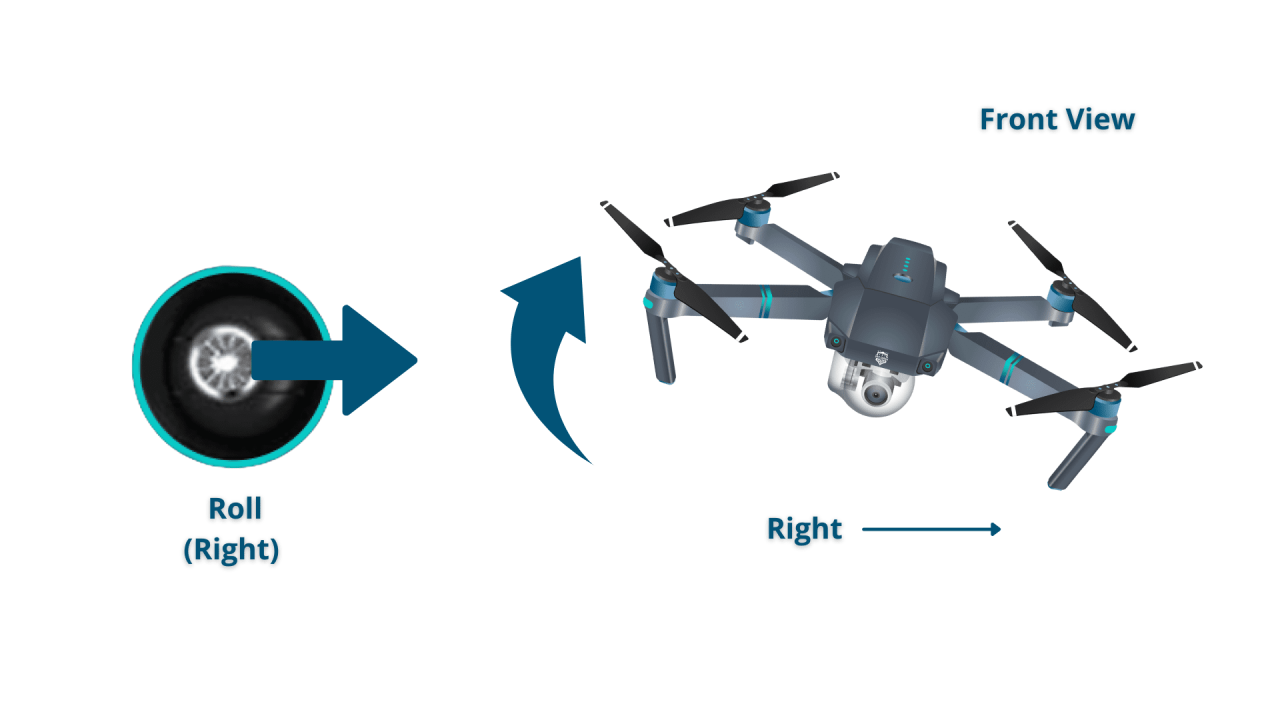
Yaw, Pitch, Roll, and Throttle Control
Yaw refers to rotation around the vertical axis, pitch is movement up and down, roll is movement side to side, and throttle controls the altitude. Understanding these four basic controls is essential for precise maneuvering.
Flight Modes
Different flight modes cater to various skill levels and situations. Beginner modes typically limit speed and responsiveness, while sport modes unlock more aggressive maneuvers. GPS modes enable autonomous flight and features like Return-to-Home (RTH).
| Flight Mode | Description | Speed | Stability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beginner | Limits speed and responsiveness for easier control | Low | High |
| Sport | Unlocks higher speeds and more aggressive maneuvers | High | Medium |
| GPS | Enables autonomous flight and features like RTH | Variable | High |
| Manual | Full manual control with no assistance | Variable | Low |
Advanced Flight Techniques and Features
Beyond basic flight controls, drones offer advanced features that enhance capabilities and expand creative possibilities. This section explores GPS-assisted flight, autonomous functions, camera modes, and advanced maneuvers.
GPS for Autonomous Flight and Waypoint Navigation
GPS allows for autonomous flight by enabling the drone to maintain its position and follow pre-programmed routes. Waypoint navigation involves setting specific points for the drone to fly to, creating complex flight paths. This feature is particularly useful for aerial photography and videography.
Return-to-Home (RTH) and Follow Me
RTH is a safety feature that automatically returns the drone to its home point, typically the takeoff location, in case of signal loss or low battery. Follow Me mode allows the drone to automatically follow a designated subject, such as a person or vehicle.
Camera Modes and Settings
Drones often offer various camera modes, such as photo, video, and timelapse, each with adjustable settings for aperture, shutter speed, ISO, and white balance. Understanding these settings is crucial for achieving high-quality aerial footage.
Performing a 360-Degree Aerial Shot
A 360-degree aerial shot involves capturing a full circular panorama from a fixed altitude. This typically involves using a drone with a gimbal-stabilized camera and employing a circular flight path. Many drones offer automated features to simplify this process.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting

Regular maintenance and prompt troubleshooting are crucial for extending the lifespan of your drone and preventing unexpected issues. This section provides guidance on maintenance schedules, common malfunctions, and troubleshooting tips.
Maintenance Schedule
A regular maintenance schedule should include inspecting the drone for physical damage after each flight, cleaning the propellers and drone body, checking the battery health, and lubricating moving parts as needed. More extensive maintenance, such as replacing worn-out parts, should be performed periodically according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Causes
Common drone malfunctions include low battery warnings, connectivity problems, motor failures, and GPS signal loss. These issues can often be traced to factors such as improper battery charging, interference from other electronic devices, worn-out components, or environmental conditions.
Troubleshooting Tips
Troubleshooting tips include checking battery levels, restarting the drone and remote controller, verifying proper Wi-Fi or Bluetooth connections, and checking for physical obstructions or interference. If problems persist, consult the drone’s manual or contact the manufacturer’s support.
Common Drone Problems and Solutions

- Problem: Low battery warning. Solution: Charge the battery.
- Problem: Drone unresponsive. Solution: Restart the drone and remote controller.
- Problem: Poor GPS signal. Solution: Fly in an open area with a clear view of the sky.
- Problem: Motor failure. Solution: Inspect and replace the faulty motor.
Drone Photography and Videography
Drones provide unique perspectives for capturing stunning aerial photography and videography. This section offers guidance on achieving smooth shots, setting up camera angles, adjusting settings, and creating compelling visuals.
Achieving Stable and Smooth Aerial Shots
Stable and smooth aerial shots require careful piloting, utilizing the drone’s gimbal (if equipped), and selecting appropriate camera settings. Avoid sudden movements and maintain a steady hand on the controller.
Setting Up Camera Angles and Perspectives
Experiment with different camera angles and perspectives to capture unique and visually appealing shots. Consider using low angles to emphasize scale, high angles for wide shots, and side angles for dramatic perspectives.
Adjusting Camera Settings
Adjusting camera settings like aperture, shutter speed, and ISO is crucial for achieving optimal image quality. Understanding the interplay of these settings is essential for capturing well-exposed and sharp images and videos in varying lighting conditions.
Examples of Creative Aerial Shots
Examples of creative aerial shots include sweeping panoramas, cinematic tracking shots, and dynamic close-ups. These can be achieved through careful planning, precise piloting, and creative use of camera settings.
Ethical and Legal Considerations
Responsible drone operation requires a strong awareness of ethical and legal considerations. This section discusses ethical implications, legal requirements, and the importance of respecting privacy.
Ethical Implications of Drone Usage
Ethical considerations include respecting privacy, avoiding intrusive surveillance, obtaining permission before flying over private property, and being mindful of the impact on the environment and wildlife.
Legal Requirements for Drone Flights
Legal requirements vary by location but often include registration, licensing, and obtaining permits for commercial operations or flights in restricted airspace. Always check local regulations before flying.
Respecting Privacy and Avoiding Intrusive Surveillance
Respecting the privacy of individuals is paramount. Avoid flying drones over private property without permission and refrain from recording individuals without their consent. Be aware of local laws concerning data privacy and surveillance.
Examples of Responsible and Ethical Drone Operation
Examples of responsible and ethical drone operation include obtaining necessary permits, flying within legal limits, respecting privacy, and maintaining visual line of sight. Always prioritize safety and responsible behavior.
Mastering drone operation requires a blend of technical understanding and responsible practice. This guide has provided a foundation for safe and effective drone piloting, equipping you with the knowledge to navigate the skies confidently and ethically. Remember to always prioritize safety, respect regulations, and continue learning to expand your capabilities and enjoy the exciting world of drone technology.
Essential Questionnaire
What is the typical flight time of a drone battery?
Flight time varies greatly depending on the drone model, battery size, and flight conditions. Expect anywhere from 15 to 30 minutes on a single charge, but always check your drone’s specifications.
How do I know if my drone needs calibration?
Signs of needing calibration include erratic flight behavior, drifting, or inaccurate compass readings. Consult your drone’s manual for specific calibration instructions.
What happens if I lose signal with my drone?
Most modern drones have a Return-to-Home (RTH) function that will automatically return the drone to its starting point. However, always fly within visual line of sight and in an open area to minimize the risk of signal loss.
Can I fly my drone in any location?
No. Drone regulations vary by location and airspace restrictions exist near airports and other sensitive areas. Check local regulations before flying.
